Digital transformation
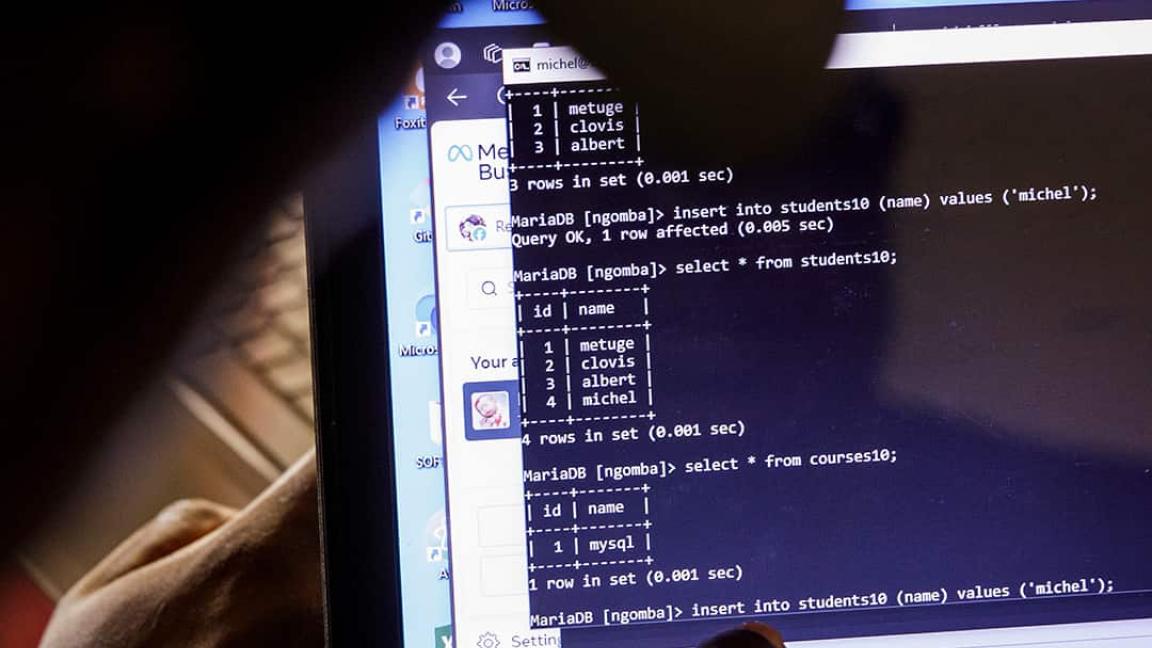
GIZ supports countries worldwide in shaping digital transformation so that it benefits everyone – making it fair, secure, sustainable and focused on people’s needs.
Our skills and expertise
-
Shaping framework conditions
We support governments in developing and implementing digital strategies – with a human rights-based approach that is transparent and participatory.
-
Putting data to good use
We use data for planning, controlling and monitoring – this makes our work efficient and responsible.
-
Facilitating digital learning
We combine digital platforms with strategic skills development – taking an individual, organisational and systemic approach.
-
Developing partnerships
Our long-standing experience locally makes us an innovative partner for German and international (digital) business, science and research and society.
-
Using technology effectively
We promote digital solutions that benefit society – from AI and e-learning through to open-source applications.



Projects in focus


